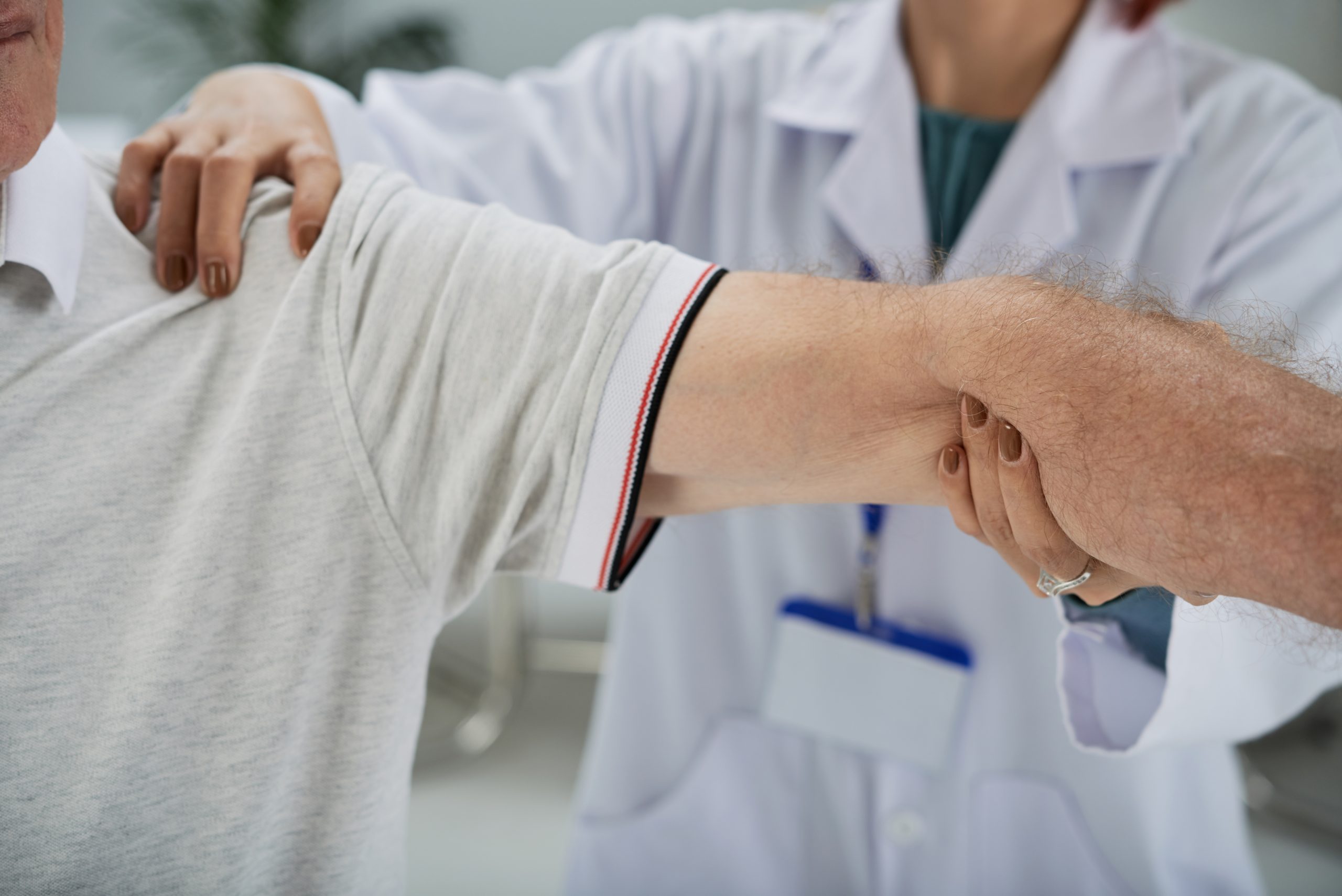
Shoulder tendonitis is one of the most common conditions in individuals who perform repetitive arm movements, whether through sports, work, or daily activities. This condition occurs when the tendons connecting muscles to bone become inflamed or irritated, causing pain and limited range of motion.
What is Shoulder Tendonitis?
Shoulder tendonitis primarily affects the rotator cuff tendons or the biceps tendon. These tendons play a crucial role in the stability and movement of the shoulder joint.
Most Common Symptoms:
- Pain in the front or side of the shoulder, which may radiate down the arm.
- Discomfort when lifting the arm, reaching for objects, or performing overhead movements.
- Stiffness or a "catching" sensation in the shoulder.
- Muscle weakness.
Common Causes
- Repetitive Use: Activities involving repetitive arm motions, such as swimming, throwing, or painting.
- Overload: Incorrectly lifting heavy objects.
- Acute Injuries: Direct impacts or falls.
- Degenerative Factors: Natural wear and tear of the tendons associated with aging.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of shoulder tendonitis begins with a detailed clinical evaluation. The physician reviews the patient’s medical history and symptoms, and performs physical tests to assess range of motion and localize the pain.
Diagnostic Imaging:
- X-rays: To rule out other conditions, such as bone spurs or arthritis.
- Ultrasound: To visualize inflammation or tears in the tendons.
- MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging): In more complex cases, to obtain detailed images of soft tissues.
Treatment Options
The goal of treatment is to reduce pain, control inflammation, and restore shoulder function.
1. Conservative Treatment:
- Rest: Avoiding activities that aggravate symptoms.
- Ice or Heat Therapy: To alleviate pain and swelling.
- Medication: Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen.
- Physical Therapy: Stretching and strengthening exercises to improve mobility and prevent future injuries.
2. Advanced Treatment:
- Injections: Corticosteroid injections to reduce inflammation in severe cases.
- Regenerative Therapies: Treatments such as Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) to accelerate tissue healing.
3. Surgical Treatment:
In cases where symptoms persist despite conservative treatment, surgical intervention - such as arthroscopy - may be necessary to repair damaged tendons or remove inflamed tissue.
Effective Recovery
Recovery from shoulder tendonitis varies depending on the severity of the injury and the treatment plan.
Tips for a Successful Rehabilitation:
- Consistent Follow-up: Attending all physical therapy sessions and following medical instructions.
- Home Exercises: Performing recommended exercises to strengthen the shoulder.
- Preventing Relapse: Modifying movement techniques in sports or work activities.
Prevention
- Perform a proper warm-up before sports.
- Maintain correct posture at work or during physical activities.
- Avoid excessive loads on the shoulder.
Conclusion
Shoulder tendonitis can be painful and limiting, but with timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment, it is possible to regain full function and avoid complications. If you are experiencing symptoms of this condition, schedule a consultation to receive specialized care.